Many users mistakenly substitute High Voltage DC contactors with AC contactors having DC control coils simply because they share an actuation method. This is a significant error, as the two devices differ vastly in their main circuit architecture, arc-extinguishing capabilities, and intended application scope.
Difference Between DC Contactors and DC Coil AC Contactors
The fundamental distinction between these two contactors is what type of current they are designed to interrupt.
High Voltage DC Contactors
High Voltage DC Contactors are engineered exclusively for DC main circuits, specifically designed to interrupt high-voltage loads without the benefit of a natural current zero-crossing. To manage this, they feature optimized mechanisms for arc suppression, superior insulation, and environmental resistance. These capabilities make them the standard choice for high-power and safety-critical DC systems.
DC Coil AC Contactors
AC Contactors with DC coils are designed primarily for three-phase AC main circuits, utilizing a DC coil solely to ensure control compatibility with automation systems like PLCs. Unlike their high-voltage DC counterparts, these devices rely on the natural zero-crossing of alternating current to extinguish arcs. Consequently, their DC switching capability is severely restricted, limited to low-voltage auxiliary circuits rather than main power distribution.
Working Principle Comparison
How High Voltage Epoxy-Sealed DC Contactors Work
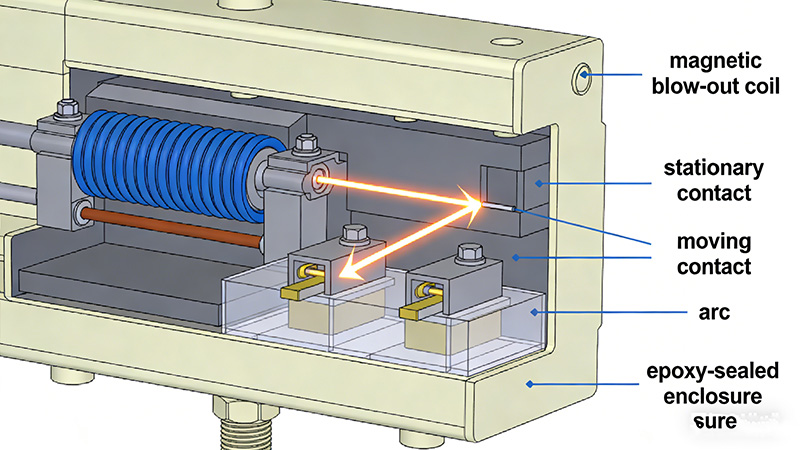
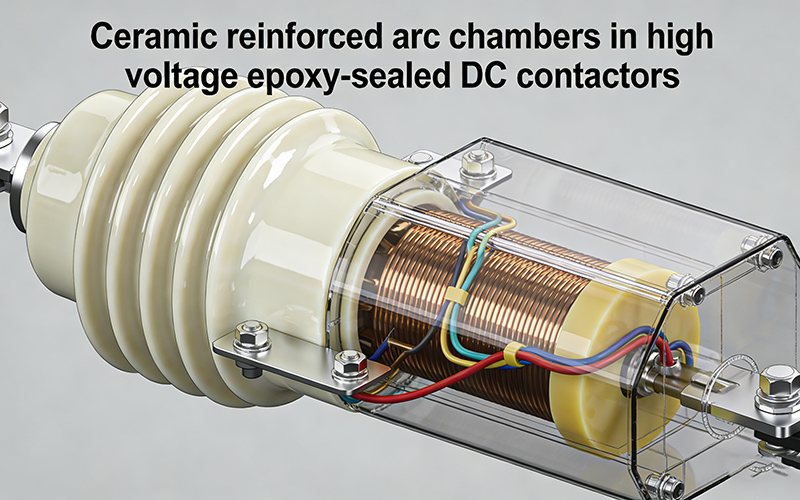
DC current does not pass through zero, which makes arc interruption extremely challenging. Epoxy-sealed DC contactors solve this problem using forced arc extinction technology, including:
- Magnetic blow-out to stretch and move the arc
- Ceramic or reinforced arc chambers
- Splitter plates to divide and cool the arc
- Full epoxy encapsulation for insulation and arc containment
This allows stable switching of high-voltage and high-current DC loads with controlled contact erosion.
How DC Coil AC Contactors Work
These devices function by combining a DC electromagnetic coil with a magnetic system and standard arc chutes engineered strictly for AC usage. Because the design relies on the natural zero-crossing of alternating current to break the circuit, the arc cannot self-extinguish when the contactor is misapplied to DC loads.
This incompatibility leads to significant failure modes, including:
- Prolonged arcing
- Rapid contact erosion
- Contact welding or catastrophic failure
Functional & Performance Comparison
| Feature | High Voltage Epoxy-Sealed DC Contactor | DC Coil AC Contactor |
| Main Circuit Type | DC only | AC only |
| Arc Extinction | Forced (magnetic + ceramic + splitter plates) | Natural (AC zero-crossing) |
| DC Switching Capability | Excellent | Very limited |
| Enclosure | Fully epoxy-sealed | Open / modular |
| Environmental Resistance | High (dust, moisture, vibration) | Standard control cabinet |
| Noise & Vibration | Silent operation | Silent (DC coil) |
| Typical Use Category | DC-1 / DC rated | AC-3 / AC-1 |
Comparative Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Epoxy-Sealed DC Contactor | DC Coil AC Contactor |
| Rated Current Range | 50A – 300A | 9A – 800A |
| Rated Voltage | Up to 1000V DC and above | AC ≤ 690V / DC ≤ 300V |
| Utilization Category | DC-1 (L/R ≤ 1 ms) | AC-3 (motors), AC-1 |
| Contact Structure | Single-pole or DC-optimized | 3-pole (3NO) |
| Installation | Stud / panel / heat sink | DIN rail / panel |
| Typical Load | DC power systems | AC motors and heaters |
| Safety in DC Systems | High | Low (not recommended) |
Application Scenarios
Epoxy-Sealed DC Contactors
Best for DC power switching
- Photovoltaic (PV) DC side
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
- EV fast charging stations (DC output)
- DC combiner boxes and DC distribution
- Electroplating and electrolysis equipment
- DC welding systems
- Rail transit and marine DC power
- Outdoor and harsh environments
DC Coil AC Contactors
Standard solution for AC loads
- Three-phase motor control (pumps, fans, compressors)
- HVAC systems
- Building automation
- Industrial production lines
- PLC-controlled AC loads
- Low-voltage DC auxiliary switching (non-critical)