Open any power control catalog and two almost identical phrases keep popping up in front of you. One line offers a switch fuse, the next one lists a fuse switch. They look like simple word games, yet behind those small changes in order sit two slightly different designs.
Both can work as a fuse disconnect switch. Both can live in the same system as a 200 amp fused disconnect on a main feeder, a 30 amp non fused disconnect on a small machine and a non fusible ac disconnect beside an outdoor unit. The trick is understanding how each one is built and how it behaves so you can pick the right style instead of guessing from a product photo.
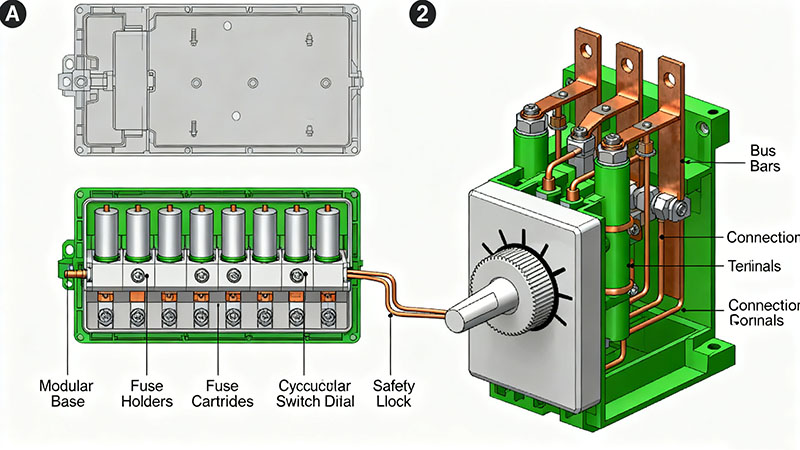
What does switch fuse mean?
Think of a switch fuse as a classic switch that has invited fuses to join it. The switch body is the main structure. Inside it you find moving and fixed contacts that carry the load current and open cleanly when the handle is turned to off, giving full load isolation.
Around that body sit the fuses. They rest in clips or small carriers that line up with the switch terminals. Current flows through them in series with the contacts, but they are not part of the moving mechanism. When it is time to replace a link, the technician opens the door, pulls the fuse out of its holder and slots a new one in place. The switch mechanism stays where it is, quietly waiting for the next on off operation.
So in a switch fuse, the switch is the main actor and the fuse is a removable co star. The handle clearly shows whether the circuit is on or off, while the fuse holder is the place to read ratings, inspect links and carry out replacements.
What does a fuse switch mean?
A fuse switch turns that story around. Here, the design begins with a fused carrier that moves as one piece. The fuses are mounted directly in a frame or bridge that the handle drives. When the handle moves to on, that frame travels into fixed terminals. When it moves to off, the whole fused assembly pulls away and leaves a clear air gap between line and load.
In this construction the fuses are not sitting beside the switch, they live inside the moving path. The blades that enter the jaws carry the fuse links with them. With the handle in the off position, the carrier and its links are visibly withdrawn. With the handle on, they are pressed firmly into contact with a strong, repeatable pressure and a clean wiping motion each time the device operates.
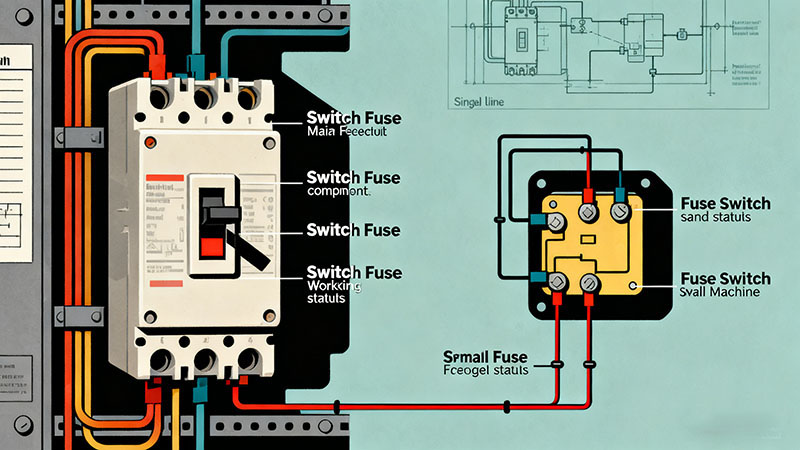
That sense of solid, visible isolation is why many designers use fuse switch products for heavier duties. A fuse switch is often chosen as the main 200 amp fused disconnect at the head of a sub board or large feeder, where the operator wants to be sure the main path is either fully made or fully open, with no halfway feeling.
Mechanical layout and operation
The difference between a switch fuse and a fuse switch is by looking at how each one is built and how it moves.
Switch fuse layout
In a switch fuse device, the parts are usually lined up on a common base. The switch contacts and the fuse holders sit in series along the same path.
- The handle drives the switch contacts. When you turn it off, those contacts open and break the circuit.
- The fuses stay in their clips in the same place, but once the contacts are open they no longer carry current.
- To change fuses, you open the enclosure, pull out the fuse links or small carriers and push new ones into position. The switch mechanism itself does not move during this replacement.
This layout makes the switching function and the fuse links feel like two separate but connected elements.
Fuse switch layout
In a fuse switch device the fuses are part of a moving carrier. The handle does not just move contacts, it moves the whole fused assembly.
- When you turn the handle on, the carrier that holds the fuse links travels into engagement with fixed terminals.
- Many designs use knife style blades that slide into those terminals when on and pull away when off.
- Turning the handle off draws the blades and the fuse links away in one motion and creates a clear air gap between line and load.
- Fuse replacement is done with the handle in the off position by removing the links from the carrier, inserting new links and then closing the switch again.
This gives a strong sense that the entire live path is being physically withdrawn when the device is switched off.
What both layouts have in common
Both constructions can be rated for full load switching and for isolation duty. Both can serve as a fuse disconnect switch, combining manual switching with overcurrent protection in one device.
How they sit beside other disconnects in a real system
In a real installation you almost never see just one family of devices. A typical layout might look like this.
- In the main room, a fuse switch serves as the 200 amp fused disconnect feeding a distribution panel. Its moving carrier gives a strong visual cue that the main blades and fuses are either fully engaged or fully withdrawn.
- Inside that panel, several switch fuse units feed motors or sections of the board. Each one acts as a compact fuse disconnect switch with its own fuse rating suited to that branch.
- Out on the plant floor, small machines use local isolators. Many of these may be fed through a 30 amp non fused disconnect where the overcurrent protection is already handled by a breaker in the main board.
- Outside, an air conditioning condenser sits on a wall bracket, with a non fusible ac disconnect mounted right beside it. Technicians can shut down the unit locally for service, while fault protection still comes from upstream.
Seen together, switch fuse and fuse switch are simply two styles of fusible hardware in a toolbox that also includes non fused disconnects. The question is not which name sounds better, but where each style helps divide the system into sensible feeders, branches and local isolation points.
Closing thoughts on terminology and use
The phrases switch fuse and fuse switch may look like small twists of language, but they hint at very real differences in construction and feel. Once you understand the story behind the words, catalog pages become easier to read, single line diagrams are simpler to interpret and discussions with suppliers and colleagues become clearer.
You can match switch fuse or fuse switch devices to each circuit with more confidence and build systems that are not only safe and well protected, but also easier to operate and maintain over their working life.
How can we assist you?
Tell us a bit more so we can route your request to the right expert.




